0CTF2018 zerofs Writeup
Overview
zerofs.ko is a driver module of a custom filesystem.
The kernel and the module is compiled by randstruct plugin, which I found in the magic string – vermagic=4.13.0 SMP mod_unload modversionsRANDSTRUCT_PLUGIN_3c73df5cc8285309b74c8a4caaf831205da45096402d3b1a80caab1d7fa1b03a`.
run.sh and /init show that the kernel is protected by SMEP, SMAP, KASLR, kptr_restrict and dmesg_restrict.
zerofs.ko
I found the module may be modified from simplefs after the game.
By reversing zerofs.ko, I knew the blocksize is 4096 bits. The first block of the image is the superblock. It consists of magic, block_size, inode_count and free_blocks bitmap.

The second block records all of the inodes in an array. ino is inode number, and dno is the block number of the image.
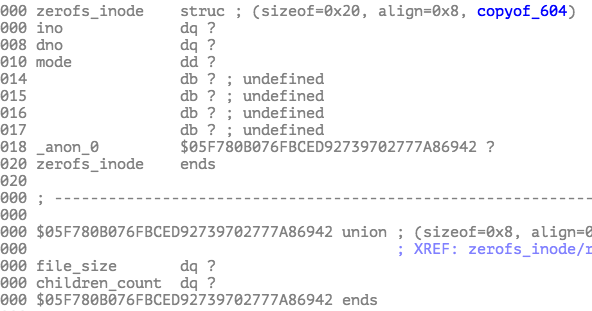
There is a root inode which ino is 1. It indicates the root dictionary. There is a block corresponding to root dictionary to indicates files in the dictionary. It is an array of zerofs_dir_record structure.

Vulnerabilitie
There isn’t any bound or size check in read and write function.
If the filesize we set in image is bigger than blocksize(0x1000), there will be an out-of-bound read/write when invoking copy_to_user/copy_from_user.
1 | unsigned __int64 __fastcall zerofs_read(file *filp, char *buf, size_t len, loff_t *ppos) |
Constructing Image
To exploit the vulnerabilities, I need to construct an malicious image. Here is the script. I put a file named 666 with size of 0xffffffffffffffff.
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python2 |
Exploit
After mounting the image, I could trigger out-of-bound read by read the file 666.
I tried to find CRED struct in leaked memory. Fortunately, I found some by searching the uid. It took me some time to locate CRED struct because of the radomization of structures.
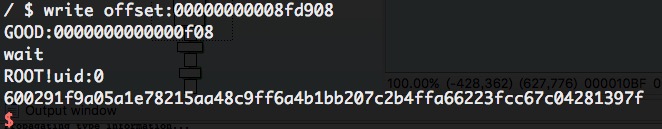
I still didn’t know which CRED is valid and which process the CRED belongs to although I could find some CRED structures. The exploit is not stable, so I run the exploit serval times. After leaking the memory, the exploit will check if it gets root privilege in a loop. If so, it invokes system("sha256sum /root/flag");.
The last step is to write the CRED. I invoked llseek to set offset to the CRED, and invoked write to modify the CRED, setting uid to 0.
Here is the expliot